Using the correct syringe is crucial to successfully managing diabetes, and insulin syringes are at the heart. But did you know that choosing the wrong needle or administering insulin incorrectly can have serious consequences?
In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about insulin syringes, from how to use them to proper disposal techniques, to ensure that you’re on the right track to successfully managing your diabetes. So, let’s dive in!
What is an insulin syringe?
An insulin syringe is a specialized medical device that is designed for the administration of insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels in the body.

These syringes are designed to be used by individuals who need to take insulin injections regularly, such as people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
Insulin syringes consist of a barrel, plunger, and a fine-gauge needle that is used to inject the insulin subcutaneously (under the skin).
The barrel of the syringe is marked with lines to indicate the number of units of insulin being drawn and injected. Insulin syringes come in various sizes and capacities, ranging from 0.3 ml to 1 ml.
These specialized syringes are crucial to the management of diabetes because they enable precise measurement of insulin doses, making it easier for individuals to maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
However, it is essential to use the correct type of insulin syringe and to use it correctly to avoid complications or errors in insulin dosage.
Types of Insulin Syringes
Insulin syringe sizes and needle sizes
Insulin syringes come in various sizes, typically ranging from 0.3 ml to 1 ml in volume.
The most common size is the 1 ml syringe, which is designed to hold up to 100 units of insulin. The size of the syringe that is used depends on the individual’s insulin dosage requirements, which can vary based on factors such as age, weight, and the severity of their diabetes.
In addition to syringe size, insulin syringes also come with different needle sizes.

The needle size refers to the length and thickness of the needle. The most common needle lengths for insulin syringes are 4mm, 5mm, 6mm, 8mm, and 12.7mm.
The thickness of the needle is measured by its gauge, with a higher gauge indicating a thinner needle.
The most common needle gauges for insulin syringes are 28G, 29G, 30G, and 31G. Thinner needles are typically preferred by patients due to their reduced pain and discomfort during injection, as well as the reduced risk of injection site reactions such as bleeding or bruising.
It is important to note that the choice of syringe and needle size should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider, as factors such as the type of insulin being used and the individual’s injection technique can also impact the appropriate choice of syringe and needle.
Differences between disposable and reusable insulin syringes
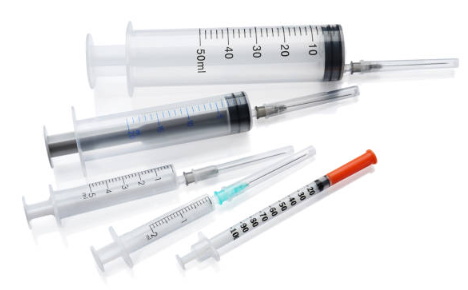
Disposable and reusable insulin syringes are two different types of syringes that are used for administering insulin injections. There are several key differences between these two types of syringes, including:
- Construction: Disposable insulin syringes are made of plastic and are designed to be used only once, whereas reusable insulin syringes are made of glass or plastic and can be used multiple times with proper cleaning and sterilization.
- Convenience: Disposable insulin syringes are pre-sterilized and come pre-filled with insulin, which makes them more convenient to use, especially when traveling. Reusable insulin syringes, on the other hand, require cleaning and sterilization between uses, which can be time-consuming.
- Cost: Disposable insulin syringes are generally less expensive than reusable syringes. While the initial cost of a reusable syringe may be higher, over time, the cost of replacing disposable syringes can add up.
- Safety: Disposable insulin syringes are designed for single-use, which helps to reduce the risk of infection and contamination. Reusable insulin syringes require proper cleaning and sterilization between uses to reduce the risk of infection.
- Environmental Impact: Disposable insulin syringes contribute to plastic waste and are not environmentally friendly, whereas reusable insulin syringes can be used multiple times and are more eco-friendly.
Overall, the choice between disposable and reusable insulin syringes will depend on an individual’s personal preferences, needs, and healthcare provider’s recommendations.
It is essential to follow proper cleaning and disposal guidelines for both types of syringes to ensure safety and reduce the risk of infection.
The U-100 insulin syringe
The U-100 insulin syringe is a type of syringe that is commonly used to administer insulin to people with diabetes.
The term “U-100” refers to the concentration of insulin in the syringe.
U-100 insulin syringes are designed to hold insulin with a concentration of 100 units per milliliter (U/mL), which is the most common concentration of insulin used in the United States.
U-100 insulin syringes typically come in three different sizes: 1cc (or 1mL), 0.5cc (or 0.5mL), and 0.3cc (or 0.3mL).
The size of the syringe will depend on the amount of insulin that needs to be administered. The needle size of a U-100 insulin syringe will also vary depending on the length and gauge of the needle.
The most common needle sizes for U-100 insulin syringes are 28 gauge, 29 gauge, and 30 gauge.
It is important to use the correct size and gauge of the needle when administering insulin to ensure accurate dosing and to reduce the risk of injection site discomfort.
U-100 insulin syringes should also be used with the corresponding insulin vial that matches the concentration of insulin in the syringe.
It is recommended to dispose of U-100 insulin syringes properly after use to prevent needle stick injuries and the spread of infections.
Many localities have specific guidelines for disposing sharps waste, including used insulin syringes, so it is important to follow these guidelines to protect public health and safety.
Overall, the U-100 insulin syringe is an important tool for people with diabetes who require insulin therapy. It is important to use these syringes correctly and to follow the guidance of healthcare professionals to ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
How to Use an Insulin Syringe
How to read an insulin syringe
Reading an insulin syringe is an important skill for anyone who needs to administer insulin. Here are the steps to read an insulin syringe:
1.Check the syringe for the correct size and gauge of the needle.
This information should be printed on the packaging or on the syringe itself.
2.Look at the syringe to find the markings on the barrel.
The barrel of the syringe is the cylindrical part that holds the insulin. The markings will be printed in units of insulin, such as 10, 20, 30, 40, etc.
3. Identify the correct dosage of insulin needed.
This will be determined by a healthcare professional and will depend on factors such as the person’s weight, blood sugar levels, and insulin sensitivity.
4. Align the top of the plunger with the marking on the barrel
that corresponds to the desired dosage. Make sure to read the dosage from the bottom of the meniscus, which is the curved surface of the insulin in the syringe.
5. Hold the syringe vertically and tap it gently to remove any air bubbles that may be present.
Push the plunger up slightly to expel any air from the syringe.
Double-check the dosage and ensure that it is accurate before administering the insulin injection.
Reading an insulin syringe accurately is essential for proper insulin administration and to ensure the safety and effectiveness of insulin therapy. It is important to receive proper training from a healthcare professional on how to use insulin syringes and to follow their guidance on dosage and administration.
How to fill an insulin syringe
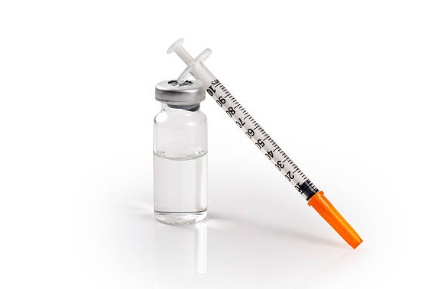
Filling an insulin syringe requires proper technique to ensure accurate dosage and safety. Here are the steps to fill an insulin syringe:
- Check the syringe for the correct size and gauge of the needle. This information should be printed on the packaging or on the syringe itself.
- Remove the cap from the needle and attach the needle to the syringe by twisting it onto the end of the syringe barrel.
- Pull the plunger back on the syringe to draw air into the syringe equal to the amount of insulin needed for the injection. For example, if the prescribed dose is 20 units, pull the plunger back to the 20-unit mark on the barrel.
- Remove the cap from the insulin vial and wipe the rubber stopper on the vial with an alcohol swab.
- Insert the needle into the rubber stopper on the insulin vial, making sure it is at a 90-degree angle. Push the plunger to inject the air into the vial.
- Turn the vial upside down and slowly pull the plunger back to withdraw the correct dose of insulin into the syringe.
- Tap the syringe gently to remove any air bubbles that may be present. If air bubbles are present, push the plunger back up slightly to expel the air.
- Double-check the dosage and ensure that it is accurate before administering the insulin injection.
Proper filling of an insulin syringe is important to ensure accurate dosage and safety. It is important to receive proper training from a healthcare professional on how to use insulin syringes and to follow their guidance on dosage and administration.
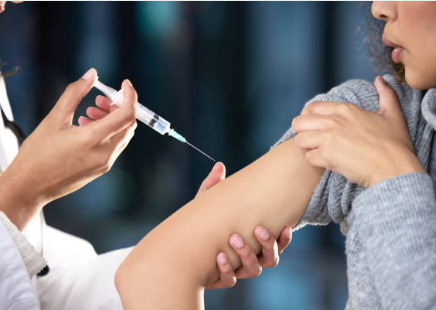
How to inject insulin with a syringe
Injecting insulin with a syringe can be intimidating at first, but with proper technique and practice, it can become routine. Here are the steps to inject insulin with a syringe:
- Choose the injection site. Common injection sites include the abdomen, thighs, and upper arms. Avoid injecting into areas that are scarred or tender.
- Wash your hands with soap and water and dry them thoroughly.
- Remove the cap from the needle and check for any air bubbles in the syringe. If air bubbles are present, gently tap the syringe to remove them and then push the plunger to expel them.
- Pinch a fold of skin at the injection site and insert the needle into the skin at a 90-degree angle. Slowly push the plunger to inject the insulin.
- Once the insulin is injected, count to five before removing the needle from the skin. This will help prevent insulin from leaking out.
- Gently press a clean cotton ball or gauze over the injection site for a few seconds to help prevent bleeding or bruising.
- Dispose of the used syringe and needle in a sharps container or follow local regulations for safe disposal.
It’s important to rotate injection sites to prevent scarring and to ensure the insulin is absorbed properly. Your healthcare provider can help you develop a rotation plan for injection sites.
If you experience any issues with injecting insulin or have concerns about your technique, talk to your healthcare provider or a diabetes educator for guidance.
How to inject insulin without pain
Injecting insulin without pain is a common concern for people with diabetes who need to administer injections on a regular basis. Here are some tips to help make insulin injections less painful:
- Use a fresh needle. Insulin needles become dull after use, which can cause more pain. Using a fresh syringe for each injection can help reduce pain.
- Inject at room temperature. Cold insulin can cause discomfort when injected. To avoid this, take the insulin from the refrigerator 30 minutes before injecting it to allow it to come to room temperature.
- Use the correct needle size. Using a needle that is too long or too thick can cause more pain. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the right needle size for your needs.
- Use a skin-numbing cream. Over-the-counter numbing creams can help reduce pain during injections. Apply the cream to the injection site 30 minutes before the injection.
- Inject slowly. Injecting the insulin too quickly can cause more pain. Slowly push the plunger to administer the insulin.
- Relax at the injection site. Tensing the muscles at the injection site can make the injection more painful. Relax the muscles by taking a deep breath and exhaling slowly.
- Use proper injection technique. Proper techniques, such as injecting at a 90-degree angle and pinching the skin before an injection, can help reduce pain.
It’s important to talk to your healthcare provider or a diabetes educator if you are experiencing pain with insulin injections. They can provide additional guidance and support to help make injections more comfortable.
Insulin Syringe Pens
What is an insulin syringe pen?
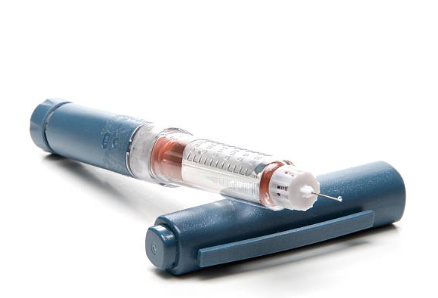
An insulin syringe pen, also known as an insulin pen, is a device used to inject insulin for people with diabetes.
It is a small, portable pen-like device that contains a cartridge of insulin and a disposable needle.
Insulin pens are designed to make it easier for people with diabetes to administer insulin injections and manage their blood sugar levels.
Insulin pens come in two types: reusable and disposable. Reusable pens are designed to be used with replaceable insulin cartridges, while disposable pens are pre-filled with insulin and discarded after use.
To use an insulin pen, the user twists off the pen cap, inserts the cartridge of insulin into the pen, and screws on a new disposable needle.
The user then dials the correct dose of insulin using a dial on the pen, primes the pen to ensure the correct amount of insulin is dispensed, and administers the injection.
Insulin pens offer several advantages over traditional insulin syringes, including ease of use, convenience, and more accurate dosing.
They are also more discreet, making it easier for people to administer insulin injections in public settings.
It’s important to note that insulin pens should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional or a diabetes educator to ensure proper use and dosing.
How to use an insulin syringe pen
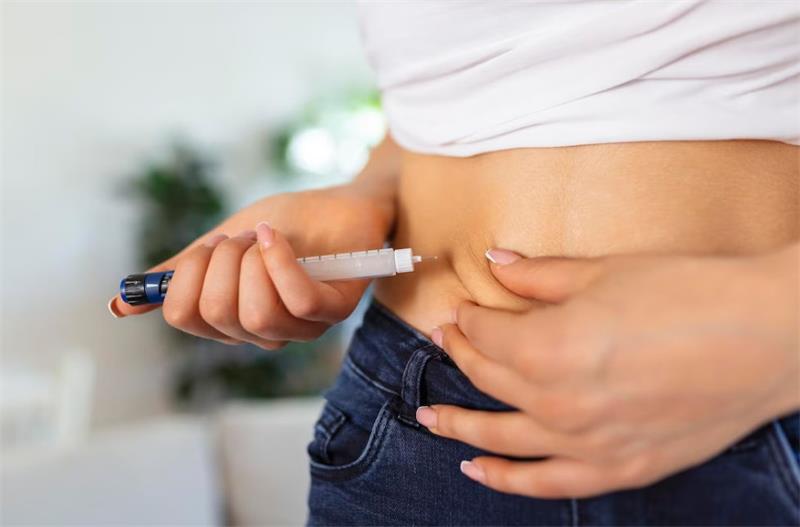

Using an insulin syringe pen to inject insulin is generally quite easy and straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use an insulin syringe pen:
- Wash your hands: Start by washing your hands thoroughly with soap and water to reduce the risk of infection.
- Assemble the pen: Take the insulin pen and remove the pen cap. Check the insulin cartridge to make sure it contains the correct type and dose of insulin. Attach the disposable needle to the pen, making sure to screw it on tightly.
- Prime the pen: Prime the pen by dialing the dose to 2 units and pressing the injection button until a drop of insulin appears at the tip of the needle. This ensures that the pen is working correctly and that the needle is properly inserted.
- Dial the dose: Dial the correct amount of insulin as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Make sure you double-check the quantity to avoid mistakes.
- Inject the insulin: Choose an injection site on your body, such as the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. Pinch a fold of skin at the injection site and insert the needle at a 90-degree angle. Press the injection button to deliver the insulin. Hold the needle in place for a few seconds to ensure that all the insulin has been injected.
- Dispose of the needle: Safely dispose of the needle and insulin pen according to your local guidelines. Some insulin pens come with a sharps container for safe disposal.
Remember to rotate your injection sites to prevent the formation of scar tissue or skin problems. And always follow the instructions of your healthcare provider or diabetes educator when using an insulin syringe pen.
Gauge and Length of Insulin Syringe
Gauge and length
Insulin syringe gauge and length are two important factors to consider when selecting the appropriate insulin syringe for your needs.
Gauge refers to the thickness of the needle, which is measured by its diameter.
The gauge of insulin syringe needles typically ranges from 28 to 31, with a higher gauge number indicating a thinner needle.
A thinner needle can be less painful, but may also take longer to inject insulin. Thicker needles can cause more discomfort during the injection but are typically faster.
The length of the insulin syringe needle is also important to consider. The length is measured from the hub of the hand to the tip.
The length of insulin syringe needles can range from 4mm to 12.7mm, with shorter needles being less painful and more suitable for people with thinner layers of body fat, while longer needles are used for people with thicker layers of body fat.
Choosing the right insulin syringe gauge and length depends on factors such as your personal preference, the type of insulin you use, and your injection technique. It’s important to talk to your healthcare provider or diabetes educator to determine the best insulin syringe gauge and length for your individual needs.
Which gauge and length to use
The choice of insulin syringe gauge and length to use depends on individual needs and preferences.
However, in general, a 30-gauge needle is the most commonly used for insulin injections, as it is thin enough to minimize pain and discomfort during an injection while still being strong enough to penetrate the skin.
When it comes to length, the appropriate length of the insulin syringe needle depends on the thickness of the layer of subcutaneous fat in the area where the injection is given.
Generally, a 4mm needle is recommended for people with thinner layers of subcutaneous fat, while a 5mm to 8mm needle is recommended for people with average-thickness layers of fat.
For people with thicker layers of subcutaneous fat, a 12.7mm needle may be necessary to reach the muscle layer.
It’s important to consult with your healthcare provider or diabetes educator to determine the appropriate gauge and length of insulin syringe for your individual needs.
They can provide guidance based on your specific health status and injection technique to help ensure safe and effective insulin administration.
How to dispose of insulin needles properly
It’s important to dispose of insulin needles properly to avoid the risk of injury and infection to yourself and others. Here are some steps to follow:
- Never re-use insulin needles. Always use a new needle for each injection.
- After use, place the used insulin needle in a sharps container immediately. Sharps containers are specifically designed to safely store used needles and protect against accidental needlestick injuries.
- Do not recap the used insulin needle. This increases the risk of accidental needlestick injuries.
- When the sharps container is full, seal it with a tight-fitting lid and label it as “used sharps.” Check with your local pharmacy or healthcare provider for guidelines on how to dispose of the full sharps container safely. Some communities offer drop-off locations for used sharps containers.
- Never throw used insulin needles in the regular trash or recycling bin. This can put sanitation workers and others at risk of injury.
By following these steps, you can help prevent the spread of infection and keep yourself and others safe.
Cost of Insulin Syringes
Insulin syringe price
The cost of insulin syringes can vary depending on the brand, type, and quantity purchased.
Generally, insulin syringes can range in price from a few dollars to several hundred dollars for bulk purchases. It’s important to note that some insurance plans may cover the cost of insulin syringes, so it’s worth checking with your insurance provider.
It’s important to note that some insurance plans may cover the cost of insulin syringes, so it’s bulk purchases.
Where to buy

When it comes to purchasing insulin syringes, there are several options available. You can buy them from a local pharmacy or medical supply store, or you can order them online from a reputable retailer. Some popular online retailers for medical supplies include Amazon, CVS, Walgreens, and Rite Aid.
It’s important to make sure you are purchasing insulin syringes from a reputable source to ensure quality and safety. Additionally, be sure to check the expiration date on the package before use, and discard any expired or damaged syringes.
When considering the cost of insulin syringes, it’s also important to remember the cost of insulin itself.
If you have diabetes, you may be prescribed insulin to help manage your blood sugar levels. Insulin can be expensive, so it’s important to work with your healthcare provider to find a treatment plan that is both effective and affordable.
Conclusion
Following insulin injection guidelines is crucial for managing diabetes and maintaining overall health.
Proper insulin injection techniques can help prevent complications such as high or low blood sugar levels, infections, and skin irritation.
Additionally, injecting insulin at the right dose and at the right time can help individuals with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels and prevent long-term complications such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and heart disease.
Finally, remember to follow insulin injection guidelines to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Proper use of insulin syringes is crucial, as using the wrong syringe or incorrect injection technique can lead to adverse health consequences.
If you have any concerns or questions about using insulin syringes, consult your healthcare provider.
In summary, insulin syringes are a vital tool in managing diabetes. By correctly selecting, using, and disposing of syringes, insulin therapy can be made more effective, and patients can better manage their diabetes.



