Curiosity fuels knowledge, and when it comes to syringes, questions abound. Whether you’re a healthcare professional, a patient, or simply someone eager to learn, we have embarked on a mission to quench your thirst for syringe-related knowledge.
What is a syringe?
A syringe is a fundamental medical tool that plays a vital role in healthcare. It is a small, cylindrical device with a hollow barrel and a plunging mechanism. Designed to administer medications, withdraw fluids, or perform various medical procedures, syringes offer precise and controlled delivery of substances into the body.

What are the different types of syringes?
Syringes come in a variety of types, each designed to cater to specific medical needs. The most common types of syringes include standard syringes, insulin syringes, tuberculin syringes, and safety syringes.
Standard syringes are widely used for various medical procedures and come in different sizes, ranging from 1 mL to 60 mL or more.
Insulin syringes, on the other hand, are specifically designed for administering insulin to diabetic patients, with markings that allow for precise insulin dosage.
Tuberculin syringes, with their slender shape and fine graduations, are commonly used for administering small doses of medication, such as in tuberculosis tests.
Safety syringes incorporate additional safety features to prevent accidental needlestick injuries, making them crucial in healthcare settings. These are just a few examples of the diverse range of syringes available, each serving specific purposes and ensuring safe and effective medical interventions.
How does a syringe work?
A syringe operates on a simple yet effective principle, allowing for precise measurement and delivery of fluids or medications. It consists of two main components: the hollow barrel and the plunger.
The barrel, typically made of plastic or glass, holds the substance to be administered. The plunger, a movable component, fits inside the barrel and creates a seal to control the flow of the substance. When the plunger is pulled back, the volume inside the barrel increases, creating a vacuum that draws the liquid or medication into the syringe.
On the other hand, when the plunger is pushed forward, the liquid is expelled through the needle. This mechanism provides healthcare professionals with control over the dosage and ensures accurate delivery.
For example, when administering medication, the plunger is pulled back to draw the correct amount into the syringe and then pushed forward to carefully inject it into the patient’s body. This simple yet ingenious design makes the syringe a versatile tool in various medical procedures.
What are syringes made of?
Syringes, the essential tools used in medical settings, are typically constructed using materials that ensure safety, durability, and ease of use. The most common materials used in syringe manufacturing are plastic and glass.
What is the purpose of a syringe plunger?
The syringe plunger serves a crucial role in the functionality of a syringe, enabling precise control over the delivery and withdrawal of fluids or medications. It is the movable component that fits inside the hollow barrel of the syringe. The primary purpose of the syringe plunger is to create a seal within the barrel, ensuring that the substance remains securely contained within the syringe until it is ready to be dispensed.
When the plunger is pulled back, it creates a vacuum, drawing fluids or medications into the barrel. Conversely, when the plunger is pushed forward, it applies pressure, facilitating the controlled release of the substance through the needle.
What is a luer lock syringe?
A luer lock syringe is a specific type of syringe that incorporates a luer lock mechanism, offering enhanced security and stability during medical procedures. It is named after its inventor, Karl August Luer, who introduced this innovative design. The distinguishing feature of a luer lock syringe is the presence of interlocking threads on the tip of the syringe barrel and the fitting of the needle or other medical devices.
These threads provide a secure and leak-proof connection, ensuring that the needle remains firmly attached to the syringe during use. This added stability is particularly beneficial in situations where there is a need for continuous or high-pressure delivery of fluids or medications.
Luer lock syringes are commonly used in various medical applications, including administering medications, drawing blood samples, and delivering contrast agents for medical imaging. The luer lock design provides healthcare professionals with confidence and reassurance, preventing accidental detachment of the needle and minimizing the risk of leakage or contamination.
What is a slip-tip syringe?
A slip-tip syringe is a type of syringe that features a smooth, tapered tip without any locking mechanism. It is commonly used in various medical procedures where a secure connection between the syringe and the needle is not essential. The slip-tip design allows for quick and easy attachment and detachment of needles or other medical devices.
To attach the needle, it is simply pushed onto the slip tip until a snug fit is achieved. Slip-tip syringes are often preferred when frequent changes of needles are required or when there is a need for rapid and efficient administration of fluids or medications.

What are the components of a syringe?
A syringe consists of several key components that work together to facilitate the safe and accurate administration of fluids or medications. The main components of a syringe include the barrel, plunger, and needle.
The barrel, typically made of plastic or glass, serves as the body of the syringe, holding the substance to be administered. It is marked with calibrated measurements to ensure precise dosage measurement.
The plunger, a movable part, fits snugly inside the barrel and creates a seal, controlling the flow of the substance. It is operated by a handle or finger grip at the top, allowing for easy manipulation.
The needle, attached to the tip of the syringe, enables the delivery of fluids or medications to the desired site. It comes in different lengths and gauges depending on the specific medical application.
Can syringes be used for multiple medications?
Syringes can be used for the administration of multiple medications, provided that certain precautions and guidelines are followed.
However, it is important to note that using the same syringe for different medications may carry risks and is generally not recommended. Mixing medications in the same syringe can lead to potential drug interactions, contamination, or dilution of the medications, which can affect their effectiveness or pose health risks.
To ensure the safe and appropriate administration of medications, it is best to use a separate syringe for each medication. This practice helps to prevent cross-contamination and ensures accurate dosing of each medication.
What is the proper technique for injecting medication using a syringe?
- Start by thoroughly washing your hands with soap and water to maintain hygiene.
- Gather all necessary supplies, including the prescribed medication, syringe, and needle.
- Check the medication label for accuracy, ensuring that it matches the prescribed dose and patient details.
- Select an appropriate needle gauge and length based on the prescribed medication and administration route.
- Clean the injection site with an alcohol swab and let it air dry.
- Remove the needle cap, being cautious not to touch the needle.
- Draw the medication into the syringe by pulling back the plunger, and aligning the desired dose with the appropriate calibration markings on the barrel.
- Remove any air bubbles from the syringe by gently tapping it and pushing the plunger to expel the air.
- Hold the syringe like a pencil or dart, with a firm grip on the barrel.
- Insert the needle into the prepared injection site at the correct angle and depth as instructed by a healthcare professional.
- Slowly push the plunger to administer the medication, ensuring a steady and controlled flow.
- Once the medication is delivered, withdraw the needle swiftly and apply gentle pressure to the injection site with a sterile cotton ball or gauze pad.
- Properly dispose of the used syringe and needle in a sharps container or as instructed by local regulations.
Remember, it is essential to follow the specific instructions provided by a healthcare professional regarding the medication, injection technique and disposal of used syringes. If any doubts or concerns arise, always consult with a healthcare provider for guidance and support.
Are syringes suitable for intramuscular injections?
Syringes are commonly used for intramuscular injections and are suitable for delivering medication into the muscle tissue. Intramuscular injections involve administering medication deep into the muscle, allowing for efficient absorption and distribution throughout the body.
The choice of syringe for intramuscular injections depends on factors such as the medication viscosity, dosage, and the patient’s specific needs. Generally, syringes with a larger capacity and longer needles are preferred for intramuscular injections to ensure proper penetration and deposition of the medication into the muscle.

Can syringes be used for intravenous injections?
Syringes are not typically used for direct intravenous (IV) injections, as there are more appropriate devices for this purpose. Intravenous injections involve delivering medication directly into the bloodstream, requiring a secure and controlled delivery system.
Specialized equipment such as IV catheters, infusion pumps, and IV bags with attached administration sets are commonly used for IV injections. These devices allow for precise dosing, proper flow rates, and continuous delivery of fluids and medications into the vein.
What is a tuberculin syringe used for?
A tuberculin syringe is a specialized type of syringe used for administering small volumes of medication, typically in the range of 0.5 mL or less. It is primarily used in diagnostic and testing procedures, such as the administration of tuberculin skin tests (TST) to detect tuberculosis (TB) infection.
How are syringes calibrated?
Syringes are calibrated using a standardized measurement system to ensure accurate medication dosing. The calibration process involves marking or engraving measurement lines on the syringe barrel to indicate the volume of medication being drawn or administered. The calibration markings are typically in milliliters (mL) and may include smaller increments for precise measurements, depending on the syringe type and purpose.
The calibration process follows strict quality control guidelines and is performed during the manufacturing of the syringe. Specialized equipment and techniques are used to achieve precise and consistent calibration.
Can syringes be used for oral administration?
Syringes are not typically used for oral administration of medications. Oral administration involves ingesting medication through the mouth, where it is absorbed by the gastrointestinal system.
While syringes are designed for precise measurement and administration of medications, they are primarily intended for injections, such as subcutaneous, intramuscular, or intravenous routes. Oral medications, on the other hand, are available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, liquids, and suspensions, which are specifically formulated for ingestion.
These formulations are designed to be swallowed and processed by the digestive system. It is important to follow the prescribed method of administration for oral medications as directed by healthcare professionals.
What are catheter tip syringes used for?
Catheter tip syringes are specialized syringes that feature a unique catheter tip design. These syringes are primarily used for specific medical procedures that involve catheterization. Catheterization is a procedure in which a thin tube, called a catheter, is inserted into a patient’s body to administer medications, and fluids, or to remove fluids or samples.
Catheter tip syringes are designed to facilitate the smooth and controlled delivery of fluids or medications through the catheter. The catheter tip of the syringe fits securely onto the catheter, ensuring a tight connection to prevent leakage or dislodgement during the procedure.
These syringes are commonly used in various medical settings, including hospitals, clinics, and home healthcare, for procedures such as urinary catheterization, intravenous infusion, enteral feeding, and drainage.
Catheter tip syringes provide healthcare professionals with a reliable and efficient tool for the precise administration and management of fluids and medications through catheters, enhancing patient care and safety.

Are syringes suitable for administering vaccines?
Yes, syringes are commonly used for administering vaccines. Vaccines are vital in preventing the spread of infectious diseases and promoting public health. Syringes provide a safe and effective means of delivering vaccines to the body. Vaccine syringes are specifically designed to meet the requirements of immunization programs.

What safety features should I consider when selecting syringes?
When selecting syringes, it is important to consider certain safety features that can enhance patient and healthcare provider safety. Here are some key safety features to look for:
Needle Safety: Opt for syringes with features like retractable needles or needle shields. These mechanisms help reduce the risk of accidental needlestick injuries and ensure safe disposal after use.
Luer Lock System: Consider syringes with a luer lock system. This feature allows for a secure connection between the syringe and needle, reducing the chances of leakage or detachment during administration.
Graduated Barrel: Look for syringes with clear and accurate volume markings on the barrel. This ensures precise measurement and dosage administration, minimizing medication errors.
Single-use Design: Choose syringes that are labeled as “single-use” or “disposable.” These syringes are intended for one-time use, reducing the risk of contamination and infection transmission.
Tamper-evident Packaging: Ensure that the syringes are sealed in tamper-evident packaging, providing assurance of product integrity and preventing unauthorized access.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards: Check if the syringes comply with relevant regulatory standards, such as ISO or FDA guidelines. This ensures that the syringes meet quality and safety requirements.
By considering these safety features when selecting syringes, you can prioritize the well-being of both patients and healthcare providers. It is essential to consult with healthcare professionals or follow institutional guidelines to choose the most appropriate syringe for specific medical procedures.
Can syringes be used for drawing blood?
Yes, syringes can be used for drawing blood in certain situations. While venipuncture is typically performed using vacuum blood collection tubes and a blood collection set, syringes can be an alternative method for blood collection in specific cases.
Syringes are commonly used when only a small amount of blood is needed or when the vein is difficult to access. In such situations, a healthcare professional may choose to use a syringe with a needle attached to withdraw the required blood volume. However, it is important to note that using syringes for blood collection requires skill and expertise to ensure accurate sampling and minimize patient discomfort.

How should syringes be disposed of safely?
Proper disposal of syringes is crucial to ensure the safety of healthcare professionals, patients, and the environment. Follow these steps to safely dispose of syringes:
Use a Sharps Container: Place used syringes and needles in a puncture-resistant sharps container immediately after use. These containers are specifically designed to prevent accidental needlestick injuries and safely contain the syringes.
Do Not Recap or Break Needles: Avoid recapping or breaking the needles after use, as this increases the risk of needlestick injuries. Dispose of the entire syringe, including the needle, into the sharps container.
Seal and Secure the Container: Once the sharps container is full, seal it tightly and secure it to prevent leaks or spills. Follow local regulations or guidelines for proper labeling and disposal methods.
Consult with Local Authorities: Contact your local health department or waste management authorities to inquire about specific regulations and guidelines for syringe disposal in your area. They can provide information on designated drop-off locations or collection programs.
Never Dispose of Syringes in Regular Trash: Do not throw used syringes in regular household or medical waste bins. This can pose a risk to sanitation workers and the environment.
By following these safe disposal practices, you can minimize the risk of needlestick injuries and prevent the improper handling or disposal of syringes. Remember, responsible syringe disposal is essential to protect public health and the environment.
What are the risks of reusing syringes?
Reusing syringes poses significant risks to both patients and healthcare providers. Here are the potential dangers associated with reusing syringes:
Contamination and Infection: Reusing syringes can introduce harmful bacteria, viruses, or other microorganisms into the body. This can lead to infections such as bloodstream infections, abscesses, or even the transmission of serious diseases like HIV, hepatitis B, or hepatitis C.
Cross-Contamination: When a syringe is reused, even if it is rinsed or cleaned, traces of previously administered medications or fluids may remain. This can result in cross-contamination and unintended mixing of substances, potentially causing adverse reactions or drug interactions.
Needlestick Injuries: Repeated use of needles increases the risk of needlestick injuries. These injuries can transmit bloodborne pathogens from one person to another, posing a significant health hazard for healthcare providers and potentially leading to infections.
Reduced Effectiveness: Reusing syringes can compromise the effectiveness of medications. Some drugs may degrade when exposed to air or when stored improperly, leading to decreased potency or ineffective treatment.
Legal and Ethical Considerations: Reusing syringes is generally considered unethical and against medical best practices. It is also illegal in many jurisdictions due to the potential harm it can cause.
To ensure patient safety and prevent the spread of infections, it is essential to always use sterile, single-use syringes for each patient and procedure. Healthcare facilities should have strict protocols in place to enforce proper disposal of used syringes and promote a culture of safety and hygiene.
Can syringes be recycled?
While some disposable syringes may be recyclable, it’s important to note that the majority of disposable syringes are not widely accepted in recycling programs. This is primarily due to safety and contamination concerns associated with used medical equipment. Syringes are typically made of a combination of plastic and metal materials, making recycling challenging.
To ensure proper disposal, it is recommended to follow local regulations and guidelines. Many healthcare facilities and pharmacies have specialized collection programs for used syringes and sharps. These programs prioritize safe handling and disposal methods to prevent injuries and the spread of infections.
What is a safety syringe?
A safety syringe is a specialized medical device designed to minimize the risk of needlestick injuries and enhance overall safety during medical procedures. It incorporates built-in mechanisms or features that help prevent accidental needle pricks after use, reducing the potential transmission of bloodborne infections.
One common type of safety syringe is the retractable needle syringe. It has a retractable needle that can be safely retracted into the syringe barrel after use, shielding the sharp point and reducing the risk of accidental needle sticks. Another type is the needle guard syringe, which includes a protective shield that covers the needle after use, effectively preventing contact with the needle.
Safety syringes are particularly crucial in healthcare settings where there is a high risk of needlestick injuries, such as hospitals and clinics. They provide added protection for healthcare professionals, patients, and others involved in medical procedures.
Are safety syringes required by law?
Yes, safety syringes are required by law in many countries to promote safer healthcare practices and reduce the risk of needlestick injuries. The specific regulations may vary from one jurisdiction to another, but the underlying goal remains the same – to protect healthcare workers and patients.
For example, in the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) requires employers to provide safety-engineered devices, including safety syringes, to employees who may be at risk of exposure to bloodborne pathogens. Similarly, the European Union has directives in place that outline the mandatory use of safety devices, including safety syringes, to prevent needlestick injuries and promote workplace safety.
What are the benefits of safety syringes?
Safety syringes offer significant benefits, including:
- Needlestick Injury Prevention: Safety syringes minimize the risk of needlestick injuries, reducing the transmission of bloodborne pathogens.
- Enhanced User Safety: These syringes incorporate features that protect healthcare workers from accidental injuries.
- Improved Patient Safety: By reducing the risk of infections, safety syringes enhance patient safety during medical procedures.
- Compliance with Regulations: Safety syringes ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and guidelines.
- Building Trust: Using safety syringes demonstrates a commitment to patient safety, fostering trust in healthcare providers.
Overall, safety syringes promote a safer healthcare environment for both healthcare workers and patients.
Can syringes be used for administering epidural anesthesia?
Syringes are commonly used for administering epidural anesthesia, a technique used to provide pain relief during labor, surgery, or certain medical procedures. Epidural anesthesia involves injecting medication into the epidural space, which is the space surrounding the spinal cord. A specialized type of syringe, known as an epidural syringe, is used for this purpose.
These syringes are designed with specific features to facilitate the precise and controlled delivery of anesthesia medications into the epidural space. The use of syringes for administering epidural anesthesia is a standard practice in healthcare settings, ensuring accurate and safe delivery of pain management medications.

What is a pre-filled syringe?
A pre-filled syringe is a ready-to-use medical device that contains a pre-measured dosage of medication or substance. It is designed to be convenient and time-saving, eliminating the need for manual drawing and measuring of medication.
Pre-filled syringes are typically filled by pharmaceutical companies or compounding pharmacies and are sealed to maintain the sterility and integrity of the medication. They are commonly used in healthcare settings, such as hospitals and clinics, for various applications including injections, vaccinations, and specialized drug administration.
The use of pre-filled syringes offers several advantages, such as accurate dosing, reduced risk of medication errors, improved patient safety, and increased convenience for healthcare professionals.
Can syringes be used for pediatric patients?
Syringes can indeed be used for pediatric patients in certain situations. Pediatric patients may require medication or vaccines that need to be administered through injections, and syringes provide a safe and effective method for delivering these treatments.
However, it’s important to consider the specific needs and requirements of pediatric patients when using syringes. For infants and young children, smaller syringe sizes with appropriate needle gauges should be used to ensure accurate dosing and minimize discomfort.
What is a glass syringe?
A glass syringe is a type of syringe that is made primarily of glass. Unlike disposable plastic syringes, glass syringes are reusable and known for their durability and accuracy. They have a transparent barrel that allows for easy visualization of the medication or substance being drawn or injected.
Glass syringes are commonly used in laboratory settings, pharmaceutical compounding, and certain medical procedures where precise measurements and sterile conditions are required. The smoothness of the glass barrel ensures smooth plunger movement, reducing the risk of medication or fluid leakage.
While glass syringes offer advantages in terms of precision and reusability, they require careful handling, proper cleaning, and sterilization to maintain their integrity. Healthcare professionals and laboratory technicians are well-versed in the appropriate techniques for using and maintaining glass syringes to ensure accurate and safe administration of medications or substances.
How do I prevent needlestick injuries when using syringes?
Preventing needlestick injuries is crucial when using syringes to ensure the safety of healthcare professionals and patients. Here are some essential tips to minimize the risk of needlestick injuries:
- Handle syringes with care: Always hold the syringe by the barrel, avoiding contact with the needle. Never recap the needle with your hands after use.
- Use safety-engineered syringes: Consider using safety syringes with built-in mechanisms to protect against accidental needlesticks, such as retractable needles or needle shields.
- Dispose of used syringes properly: Immediately after use, place used syringes in designated sharps containers. Avoid overfilling and never dispose of syringes in regular trash bins.
- Follow proper sharps disposal guidelines: Adhere to local regulations and guidelines for the disposal of sharps waste. This helps prevent injuries to waste handlers and minimizes environmental risks.
- Use needlestick prevention devices: Utilize safety devices like needlestick prevention caps or devices that can cover the needle securely after use.
- Educate and train healthcare staff: Provide comprehensive training to healthcare professionals on safe syringe handling techniques, including proper disposal practices and the use of safety devices.
- Implement sharp injury prevention protocols: Establish workplace protocols that prioritize the use of safety-engineered devices, provide education, and promote a culture of safety to prevent needlestick injuries.
By following these preventive measures, healthcare professionals can significantly reduce the risk of needlestick injuries, ensuring a safer healthcare environment for all.
Can syringes be used for administering contrast agents in medical imaging?
Yes, syringes are commonly used for administering contrast agents in medical imaging procedures. Contrast agents are substances that enhance the visibility of certain tissues or organs during imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs.
Syringes offer precise control over the amount of contrast agent administered, ensuring accurate dosing for optimal imaging results. The contrast agent is drawn into the syringe and then carefully injected into the patient’s bloodstream or specific body cavity, depending on the imaging technique used.
What is a retractable needle syringe?
A retractable needle syringe is a type of syringe that automatically retracts the needle into the syringe barrel after use. It minimizes the risk of needlestick injuries and enhances safety for healthcare workers and patients.
Incorporating this safety feature reduces the chances of accidental needlestick and potential exposure to bloodborne pathogens. Retractable needle syringes are widely used in healthcare settings to promote safer injection practices and prevent the transmission of bloodborne diseases.
Are there alternatives to syringes for medication administration?
Yes, there are alternatives to syringes for medication administration. Depending on the specific medication and route of administration, various alternatives can be used. Some common alternatives include oral medications in the form of tablets or capsules, transdermal patches, inhalers for respiratory conditions, and intravenous infusion pumps.
Additionally, specialized devices such as auto-injectors and nasal sprays are available for specific medications. The choice of an alternative depends on factors such as the medication’s formulation, the patient’s condition, and the desired therapeutic outcome.
Healthcare professionals can determine the most appropriate administration method based on individual patient needs and medical guidelines.
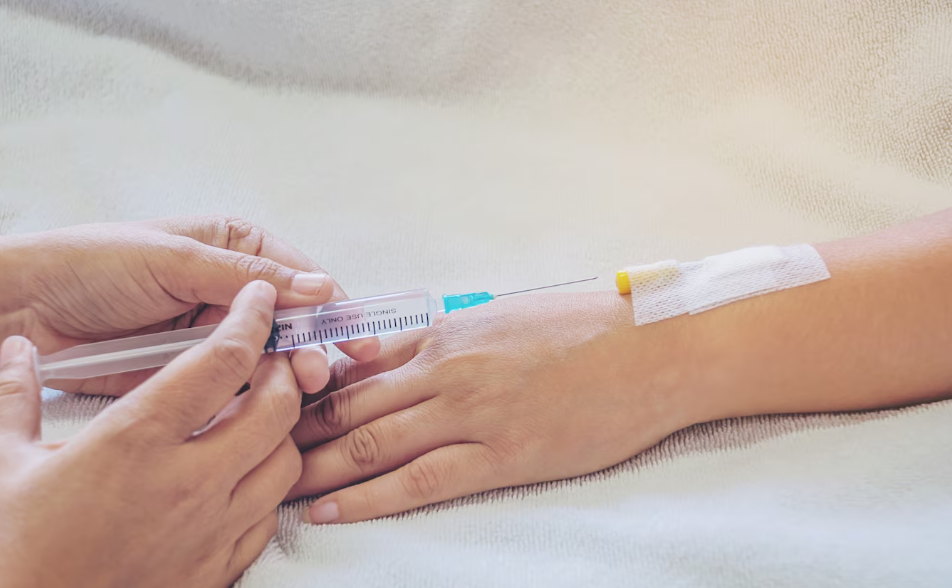
Can syringes be used for intradermal injections?
Yes, syringes can be used for intradermal injections. Intradermal injections involve administering medication into the dermis layer of the skin, which is just below the epidermis. This method is commonly used for skin testing, such as tuberculin tests or allergy tests.
For intradermal injections, a syringe with a small-gauge needle, typically 26 or 27 gauge, is used. The medication is injected at a shallow angle into the skin, forming a small bleb or wheal. Intradermal injections require precision and careful technique to ensure accurate results.
It is important to follow proper medical guidelines and receive training to perform intradermal injections safely and effectively.
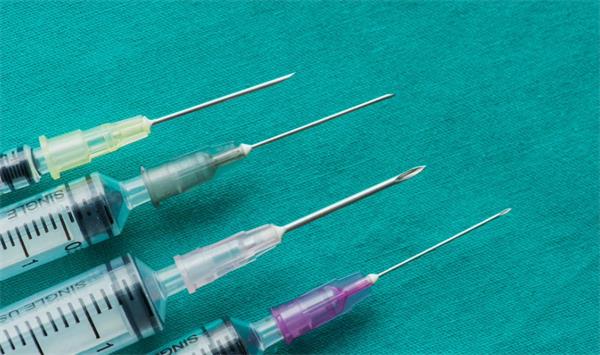
What are the different needle gauges and lengths available for syringes?
Syringes come in different sizes and needle options to accommodate various medical requirements. The volume of a syringe is typically measured in milliliters (ml). Common syringe sizes include 1 ml, 3 ml, 5 ml, and 10 ml, among others.
The needle gauge, which indicates the thickness of the needle, is denoted by a number. For example, smaller gauge numbers like 18G represent thicker needles, while larger gauge numbers like 27G represent thinner needles.
Needle lengths are measured in inches or millimeters, and they can range from 1/2 inch to 2 inches. The choice of syringe size, needle gauge, and length depends on factors such as the medication dose, the intended route of administration, and patient comfort.
It’s important for healthcare professionals to select the appropriate syringe specifications to ensure accurate dosing and patient safety.
Are syringes suitable for administering chemotherapy drugs?
Syringes are commonly used for administering chemotherapy drugs. Chemotherapy is a treatment method that uses powerful medications to target and destroy cancer cells.
Syringes provide an efficient and precise way to deliver chemotherapy drugs into the patient’s body. The healthcare professional carefully measures the required dose of the medication and administers it through a syringe, usually via injection into a vein or a port.
The use of syringes allows for accurate dosing and helps ensure that the chemotherapy drugs reach their intended target. It’s important to note that chemotherapy administration should always be performed by trained medical personnel following established protocols to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Can syringes be used for administering local anesthesia?
Yes, syringes are commonly used for administering local anesthesia. Local anesthesia is a type of anesthesia that numbs a specific area of the body, typically for minor surgical procedures or dental work.
Syringes provide a precise and controlled way to deliver the anesthesia medication to the targeted area. The healthcare professional carefully measures the appropriate dose of the anesthesia drug and administers it using a syringe, often through injection or infiltration near the site that requires numbing.
The use of syringes allows for accurate dosage and ensures that the anesthesia takes effect in the desired area. It’s important to note that the administration of local anesthesia should always be performed by trained medical professionals following established guidelines and safety protocols.

How do I ensure accurate medication dosing with a syringe?
Ensuring accurate medication dosing with a syringe is essential for patient safety and effective treatment. Here are some important steps to follow:
- Read and understand the medication instructions: Carefully review the prescription or medication label to understand the prescribed dosage, concentration, and any specific instructions.
- Use the appropriate syringe size: Select a syringe that is suitable for the volume of medication you need to administer. Make sure the syringe has clear markings that allow for accurate measurement.
- Measure the medication carefully: Use the syringe to draw the medication, following the prescribed dosage. Pay close attention to the volume markings on the syringe and fill it accurately.
- Eliminate air bubbles: To ensure accuracy, gently tap the syringe to dislodge any air bubbles, and then push the plunger slowly to release any trapped air. This will help you measure and administer the correct amount of medication.
- Administer the medication correctly: Choose the appropriate route of administration (e.g., intramuscular, subcutaneous, or intravenous) as instructed by the healthcare professional. Inject the medication slowly and steadily, taking care to follow the recommended technique.
- Double-check the dosage: Before administering the medication, double-check the dosage calculations and compare it with the prescribed amount. Ensure that you have accurately measured the medication and that the dosage aligns with the prescription.
- Dispose of the syringe properly: Once you have administered the medication, dispose of the syringe safely according to medical waste disposal guidelines.
By following these steps, you can help ensure accurate medication dosing with a syringe, minimizing the risk of errors and promoting patient safety. Always consult with a healthcare professional for specific instructions and guidance regarding medication administration.
Can syringes be used for administering hormonal contraceptives?
Yes, syringes can be used for administering hormonal contraceptives. Hormonal contraceptives, such as injectable contraceptives, are often administered using syringes. These contraceptives contain hormones that help prevent pregnancy by inhibiting ovulation or thickening the cervical mucus.

Are there any limitations to using syringes for medication administration?
While syringes are versatile tools for medication administration, there are certain limitations to consider. One limitation is the accuracy of dosage measurement, especially with small volumes. It is important to ensure precise measurement and avoid dosing errors. Additionally, some medications require specialized delivery systems, such as auto-injectors or infusion pumps, which may not be compatible with standard syringes.
Another limitation is the need for proper training and technique when using syringes. It is essential to have the necessary knowledge and skills to handle syringes safely and administer medications correctly. This includes proper needle insertion, injection site selection, and proper disposal of used syringes to prevent needlestick injuries and contamination.
Furthermore, certain medications may have specific administration requirements that cannot be met with standard syringes alone. For example, certain biologic drugs require specialized delivery devices to ensure proper handling and administration.
What is a slip tip syringe adapter?
A slip tip syringe adapter is a device that is used to enhance the functionality and versatility of slip tip syringes. It is a removable attachment that connects to the tip of the syringe, providing additional features or capabilities.
The adapter typically has a different design or mechanism that allows for specific functions, such as precise dosage control or compatibility with different needle sizes.
Can syringes be used for administering intranasal medications?
Yes, syringes can be used for administering intranasal medications. Intranasal administration involves delivering medications through the nostrils, where they are absorbed into the bloodstream through the nasal mucosa. This method is commonly used for medications such as nasal sprays or nasal drops.
To administer intranasal medications using a syringe, a specific device called a nasal atomizer or nasal adapter is often attached to the syringe. The nasal atomizer converts the liquid medication into a fine mist, allowing for easier and more effective delivery into the nasal cavity.
How do I choose the right needle size for a syringe?
When choosing the right needle size for a syringe, there are a few factors to consider. The needle size is determined by its gauge and length, which impact the flow rate and penetration depth.
Gauge refers to the thickness of the needle, and it is represented by a numerical value. The smaller the gauge number, the larger the needle diameter. Common needle gauges range from 30G (thinnest) to 18G (thickest). Thinner needles are suitable for medications that require a more precise and controlled flow, while thicker needles are used for viscous substances or when a faster flow rate is needed.
The needle length is measured in inches and determines how deep the needle penetrates into the tissue. Shorter needles, such as ½ inch or 5/8 inch, are typically used for subcutaneous injections (into the fatty tissue just below the skin), while longer needles, like 1 inch or 1.5 inches, are used for intramuscular injections (into the muscle) or other deeper injections.
The appropriate needle size depends on various factors, including the patient’s age, body habitus, injection site, medication viscosity, and the intended route of administration. Healthcare professionals, such as doctors or nurses, can guide you in selecting the right needle size based on these considerations.
What are the uses of syringes in the laboratory?

Syringes play a vital role in laboratory settings and have various uses across different scientific disciplines. In the laboratory, syringes are commonly employed for precise and controlled liquid handling tasks. Here are some of the primary uses of syringes in laboratory settings:
- Sample Transfer: Syringes are utilized to transfer small volumes of liquids, such as samples, reagents, or solvents, from one container to another. The precise measurement capabilities of syringes enable accurate volume dispensing, reducing the risk of errors.
- Solution Preparation: Syringes are essential for preparing solutions with precise concentrations. By accurately measuring the required volumes of solutes and solvents, syringes allow scientists to create solutions with the desired concentrations for experiments and analyses.
- Extraction and Filtration: Syringes equipped with filters or specialized needles are employed for extracting or filtering samples. These syringes enable the removal of impurities or particulate matter, ensuring clean and purified samples for further analysis.
- Chromatography: Syringes are utilized in chromatographic techniques, such as liquid chromatography (LC) and gas chromatography (GC). They are employed to inject precise volumes of samples into the chromatography system, facilitating the separation and analysis of compounds of interest.
- Cell Culture: In cell culture applications, syringes are used for aseptic handling of media, buffers, and other solutions. They enable accurate and sterile addition of liquids to cell cultures, maintaining the integrity of the cells and minimizing contamination risks.
- Animal Studies: Syringes find applications in laboratory studies involving animals. They are used for administering substances, such as drugs or experimental compounds, to animals with precision, ensuring accurate dosing and monitoring.
It’s important to note that in the laboratory, different types of syringes may be used, including those with specialized features such as luer-lock connections or blunt-tip needles, depending on the specific requirements of the experiment or procedure.
By offering precise liquid handling capabilities, syringes are indispensable tools in laboratory settings, facilitating accurate measurements, controlled dispensing, and ensuring reliable experimental outcomes.
Where can I get syringes?
When it comes to obtaining syringes, there are various options available to ensure accessibility and safety. Here are some common avenues where you can acquire syringes:
Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies are primary sources for obtaining syringes. They have trained professionals who can provide the appropriate syringes based on your needs. You may need a prescription for certain types of syringes, so consulting with a healthcare provider is recommended.
Online Pharmacies: Many reputable online pharmacies offer syringes for purchase. Ensure that you choose a reliable and licensed online pharmacy to ensure the quality and safety of the syringes.

Medical Supply Stores: Local medical supply stores often carry a wide range of syringes. These stores cater to healthcare professionals and individuals who require medical supplies. You can find various types and sizes of syringes based on your specific requirements.
Community Health Programs: Some community health programs or harm reduction initiatives provide syringes as part of their services. These programs aim to promote safe injection practices and prevent the spread of diseases. They may offer free or low-cost syringes in a confidential and supportive environment.
Remember, it is important to follow local regulations and guidelines regarding the purchase and use of syringes. If you have specific medical needs or are unsure about the appropriate syringe for your situation, consult with a healthcare professional who can guide you in obtaining the right syringes safely and legally.
Which country makes the most syringes?
When it comes to syringe production, several countries are known for their significant manufacturing capabilities. While it is challenging to pinpoint a single country that makes the most syringes, some nations play a prominent role in the global syringe manufacturing industry. These countries include:
China: China has emerged as a major manufacturer of syringes due to its large-scale production facilities and advanced manufacturing technologies. Many companies in China specialize in the production of syringes and export them worldwide.
United States: The United States has a robust medical device industry, including syringe manufacturing. Numerous companies in the U.S. are involved in producing syringes to meet the demand of the domestic market and for export purposes.
Germany: Germany is renowned for its precision engineering and high-quality medical devices. Several German manufacturers produce syringes, focusing on precision, reliability, and adherence to stringent quality standards.
India: India has a significant presence in the syringe manufacturing industry. The country has a large number of syringe manufacturers catering to both the domestic and international markets. Indian manufacturers often offer cost-effective solutions while maintaining quality standards.
Japan: Japan is known for its advanced healthcare technology and innovation. Japanese manufacturers produce a range of syringes with a focus on precision, safety, and user-friendly features.
It’s worth noting that many other countries also contribute to syringe production, and the global market is diverse and dynamic. The choice of the country manufacturing the most syringes may vary depending on factors such as market demand, manufacturing capabilities, and industry trends.
What is the best brand of syringe?
When it comes to choosing the best brand of syringe, there are several reputable options available in the market. These brands have earned a strong reputation for their quality, reliability, and user-friendly features. Here are the five top syringe brands to consider:
BD (Becton, Dickinson, and Company): BD is a renowned brand known for its wide range of medical devices, including syringes. They offer high-quality syringes in various sizes and configurations to meet different medical needs.
Terumo: Terumo is a trusted name in the medical industry, particularly in the field of syringe manufacturing. Their syringes are known for their precision, smooth operation, and advanced safety features.
Nipro: Nipro is a global healthcare company that produces a diverse range of medical devices, including syringes. Their syringes are designed for accurate dosing, ease of use, and patient comfort.
Smiths Medical: Smiths Medical is a leading manufacturer of medical devices and syringe systems. Their syringes are known for their quality, durability, and innovative design features that enhance safety and ease of use.
Covidien (now Medtronic): Covidien, now part of Medtronic, is a well-established brand in the healthcare industry. They offer a wide range of syringes that are designed to deliver precise medication dosing and ensure patient safety.
It’s important to note that the choice of the best syringe brand may vary depending on specific requirements, healthcare settings, and personal preferences. It’s recommended to consult with healthcare professionals or refer to user reviews and feedback when making a decision.
Is a syringe biodegradable?
Syringes are typically made from plastic materials such as polypropylene or polycarbonate. These materials are not biodegradable in the traditional sense, meaning they do not naturally break down into the environment over time. However, there are initiatives and advancements in the field of sustainable materials that aim to develop biodegradable alternatives for syringes.
Some manufacturers are exploring the use of biodegradable plastics, such as PLA (polylactic acid), which is derived from renewable resources like cornstarch or sugarcane. These biodegradable syringes are designed to break down more readily under specific environmental conditions, reducing their long-term impact on the environment.
Is the insulin syringe disposable?
Yes, insulin syringes are typically designed for single use and are considered disposable. This means that after a single injection, the syringe is intended to be discarded and not reused. Using a new syringe for each insulin injection helps maintain proper hygiene, reduces the risk of contamination, and ensures accurate dosing.
What are the disadvantages of using a syringe?
- Risk of needlestick injuries: Improper handling of syringes can lead to accidental needlestick injuries, posing risks to healthcare professionals and patients.
- Need for proper training and technique: Accurate dosing and administration with syringes require proper training and technique to ensure precise medication delivery and avoid potential errors.
- Potential for contamination: If syringes or their contents are not handled and stored correctly, there is a risk of contamination, which can compromise patient safety and treatment efficacy.
- Limitations in administration routes: Syringes may not be suitable for all medication administration routes, requiring alternative methods or devices for specific applications.
- Generation of medical waste: Syringe use contributes to the generation of medical waste, requiring proper disposal methods to minimize environmental impact and ensure safety.
Despite these disadvantages, it’s important to note that with appropriate education, training, and adherence to safety protocols, syringes remain an essential and effective tool in various healthcare and laboratory settings.